Budget at Completion formula PMP® Exam Topic
One of the critical concepts within the Earned Value area of formal project management is Budget at Completion (BAC). The Project Management Institute (PMI)’s Project Management Professional (PMP)® certification exam may include questions about, or driven by, the earned value (EV) performance calculations, including BAC. The great news is there is not a Budget at Completion formula to learn. For project managers seeking the “PMP BAC definition,” it is this: the original project budget.

PMP® Exam Formula Cheat Sheet
Learn how to successfully use project management formulas after reading this cheat sheet.
Determine Budget at Completion (BAC)
The PMI’s A Guide to Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) – Sixth Edition, includes control cost processes enabling forecasting of the project’s completion from a budgetary lens. The PMBOK® Guide gives this definition of BAC: “the sum of all budgets established for the work to be performed.” At the most basic level for example, if the original project budget is $25,000, then the project’s BAC is $25,000. Another way to think of the Budget at Completion formula “is the value that PV is planned to reach at completion.”

Rather than thinking of the concept as the “BAC PMP formula,” it should be viewed as understanding what Budget at Completion is as a definition and how to determine it. Consider these elements for the Budget at Completion value:
- Determined at project start based on work planned
- Used with Planned Value (PV) to determine budget’s status against planned
- Compared to Estimate at Completion (EAC) at point of analysis based on expected future work
- Expressed in cost units (any currency)
Although there is not a BAC formula, the BAC value is used in many Earned Value formulas. The accuracy of the BAC has many downstream impacts within the Earned Value calculations. There are three main techniques for determining the BAC: analogous estimation, expert judgment, and parametric estimation.
Analogous Estimation
An analogy is where you take one idea to explain or clarify something similar. The comparison of like things to find meaning, or in the project management context, budget, can be forecasted as an analogous estimation.
| BAC Technique | Analogous Estimation | Match a project’s tasks and deliverables to a similar project’s tasks and deliverables; use the actual costs from the matched project to determine BAC |
The BAC technique of analogous estimates can help with projects in which there is limited information for the current work if the project manager has a deep understanding of the current work and the compared work. Rather than spending time researching and trying to figure out everything from the beginning, analogous estimation is a way to “fast track” budgeting and leverage the actual and known costs of a previous project.
And yet, Project Managers must have a strong understanding of their project to successfully use Analogous Estimation, because if the project compared is not similar or does have enough similarities, the estimate may lead to problems later. Or, there may not be a project of a similar nature in which budgets can be compared. In those instances, project managers should find similarities where they can, in terms of segments of past work, work activities from past work, or similar materials from past work.
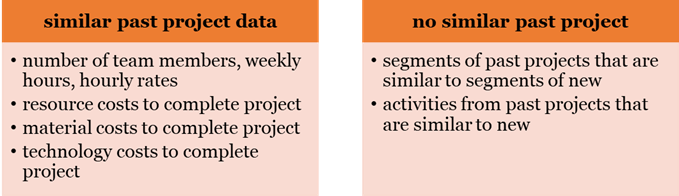
As part of the PMP certification exam questions about BAC, project managers may be asked when to use analogous estimation to determine BAC.
Expert Judgement
Project managers looking to establish a BAC will sometimes depend on the input of experts to determine the budget at completion. This BAC technique is known as “expert judgment.”
| BAC Technique | Expert Judgement | Obtain estimates from experts and subject matter experts knowledgeable of the project’s components and costs |
The expertise of the subject matter expert can be based on the “training or educational background, career experience, or knowledge of the product/market.”

When using Expert Judgment as a way to determine Budget at Completion, include groups with specialized skills such as professional organizations or industry associations. These experts can provide ideas and the probability of occurrence based on experience. There is not a formal method for establishing BAC when getting information from the experts, but there are commonly used approaches for data collection: brainstorming with a group of experts, interviewing experts, sending targeted surveys to experts.
Conducting interviews and brainstorming sessions can be an extended process that can take some time. It is also possible the expert will give faulty estimates to present a more efficient project than was the actual case. On the good side, the budget estimate could be more accurate due to the insights and lessons learned from the expert.
Parametric Estimation
The BAC definition encompasses the “Parametric estimation” technique. For estimates of budget, cost, and project duration, the project manager will “break down the project into sub-components and match them with the appropriate equation to obtain the estimates.”
| BAC Technique | Parametric Estimate | The statistical relationship between historical data and variables |
Consider this example from plainsware.com of a parametric estimate for budget at completion:
Let’s say your project includes carrying out a survey of 300 people. Each interview contains 20 multiple-choice questions, and past experience has shown they take 10 minutes to administer. According to parametric estimation, the total effort for this task will be:
E = nb of interviews × 10 minutes = 3000 minutes = 5 hours
A PMP® credential holder knows there several ways to source the parametric value: previous internal project, previous external project, and industry data. Access to and the quality of data from each source is dependent upon the industry and size of the company.
Pros and Cons of BAC Analysis
Those who hold the PMP® certification may look to the PMI’s resource library for insights on the BAC definition and formula. As a budget tool, the BAC is simply: “the amount of resources estimated as necessary to complete the work described in the scope statement.”
Pros of BAC Analysis
- Analogous Estimating can be conducted early in a project when not all details are very defined.
- Expert Judgement can reduce risks as it uses lessons learned from those with experience.
- Parametric Estimating can be very accurate based on actual costs of similar scope.
Cons of BAC Analysis
- Analogous estimating as the scope is more refined, the estimate must be reworked over and over.
- Expert Judgement can be biased leading to inaccuracies or blind spots in the budget estimate.
- Parametric estimating is only as accurate as the data and calculations used to determine it.
How BAC fits into Earned Value and PMP® Certification Exam
Project Managers should not simply search the term “BAC PMP” to prepare for the PMP certification exam. Instead, know BAC questions are likely to be about the BAC techniques and how BAC fits into the larger earned value practice. In the provided Earned Value Terminology chart, BAC is highlighted for easy reference.
| Actual Cost | AC | the actual cost of the project | amount spent on the project |
| Actual Cost of Work Performed | ACWP | cost of the project completed within a specific time | cost of the project completed within a specific time |
| Budget At Completion | BAC | total of budget | total of budget |
| Budgeted Cost for Work Performed | BCWP | also EV; the amount of work actually completed | % Work Complete x Budget |
| Budgeted Cost for Work Scheduled | BCWS | also PV; value of the work completed to date | Planned % complete x BAC |
| Cost Performance Index | CPI | cost variance; CPI < 1 = over budget, CPI > 1 = under budget | EV / AC |
| Cost Variance | CV | amount of project budget over or under budget; CV < 0 = over budget, CV > 0 = under budget | EV – AC |
| Earned Value | EV | also BCWP; amount of work actually completed | % Work Complete x Budget |
| Estimate at Completion | EAC | expected budget at project end based on variances that have occurred | AC + BAC – EV |
| Estimate to Complete | ETC | expected cost to finish remainder of project | EAC – AC |
| Planned Value | PV | also BCWS; value of the work completed to date | Planned % complete x BAC |
| Schedule Performance Index | SPI | schedule variance; SPI < 1 = behind schedule, SPI > 1 = ahead of schedule | EV/ PV |
| Schedule Variance | SV | amount of project work ahead or behind schedule; SV < 0 = behind schedule, SV > 0 = ahead of schedule | EV – PV |
| Variance at Completion | VAC | forecasted cost variance at end of project | BAC – EAC |
As part of the PMP certification exam questions, project managers may be asked when to use BAC which technique or be provided a scenario in which a formula for one earned value tool is needed in addition to the BAC to analyze the data.
Sample BAC PMP® Certification Exam Questions
| Question | A | B | C | D |
| You are the project manager of the Everest Consulting Project. The project has a budget of $290,000 and is expected to last three years. The project is now ten percent complete and on schedule. The project is currently $10,000 over budget. What is the BAC? | 280,000 | 290,000 | 300,000 | 870,000 |
| You are the project manager on an agile team that has been hired by a federal government agency to develop and implement a new invoicing system. As expected, the agency expects to receive periodic Earned Value reports each month that will be reviewed by senior staff. Your first report covers the work completed for the first two 2-week sprints. The numbers on the report include BAC = $500,000, EAC = $495,000, AC = $15,000, PV (based on story points) = $20,000, EV = 21,000. Which of the following is true? | The project is on schedule and over budget | The project is ahead of schedule and under budget | The project is behind schedule and over budget | The project is ahead of schedule and over budget |
Studying for the PMP Exam?
Conclusion
The Budget at Completion (BAC) is part of the Earned Value (EV) terms and formulas used by Project Managers Professionals (PMP) to manage the cost process. Although BAC does not have a formula, the BAC is needed to complete many EV formulas. Project Managers must use their own knowledge to determine which BAC technique to use for a project.
Answers
- B. The BAC is the budget at completion, which is given to you in the question.
- B. Since BAC > EAC, the project is under budget by $5000. Since EV > PV, the project is ahead of schedule (more story points were completed than planned in the first two sprints).
Upcoming PMP Certification Training – Live & Online Classes
| Name | Date | Place |


 New Horizons
New Horizons
 Project Management Academy
Project Management Academy
 Six Sigma Online
Six Sigma Online
 TCM Security
TCM Security
 TRACOM
TRACOM
 Velopi
Velopi
 Watermark Learning
Watermark Learning
 Login
Login




 New Horizons
New Horizons
 Project Management Academy
Project Management Academy
 Velopi
Velopi
 Six Sigma Online
Six Sigma Online
 TCM Security
TCM Security
 TRACOM
TRACOM
 Watermark Learning
Watermark Learning