Key Takeaways
- Clear identification: prevents overlooked roles that disrupt timelines and approvals.
- Influence awareness: ensures high-impact contributors receive early engagement.
- Structured categories: guide planning and help teams manage expectations.
- Adaptive engagement: reduces risk when signals show shifting priorities.
- Process discipline: stabilizes communication and supports consistent delivery.
Why Stakeholder Management Shapes Every Project Outcome
Stakeholder management shapes how smoothly a project moves from planning to delivery. Stakeholders influence requirements, approvals, and the pace of key decisions. When teams understand these voices early, work stays aligned. When they do not, delays often appear without warning.
At SentinelWave, a team finished a system upgrade and expected quick approval. They met their deadlines, stayed within budget, and prepared a clean handoff. Their momentum stalled when a department head said they had never been consulted. That single miss triggered questions, rework, and an unexpected pause.
This oversight showed that the team built its stakeholder list on habit instead of analysis. A missing high-influence voice was enough to interrupt progress and raise concerns. The experience made it clear that effective stakeholder work requires intention. It’s a process, not a set of quick updates.
The sections that follow explain what stakeholder management involves, why it matters, and how structured practices help teams prevent the kind of delay SentinelWave experienced.
How a Simple Stakeholder Oversight Can Spark Unexpected Delays
Stakeholder management begins with knowing who truly shapes decisions. Teams often default to familiar names, but a closer look at roles and influence reveals people who skip meetings yet still hold authority. When these voices are missed, delays can surface quickly.
Common stakeholder groups
- Sponsors: provide strategic direction and final approval authority.
- Operational leaders: guide functional changes that affect teams or workflows.
- End users: experience daily impact and clarify practical needs.
- Vendors or partners: support integration or technical components.
- Regulatory or compliance staff: ensure decisions meet policy standards.
As the team began their review, the operations director reflected on their oversight. “We documented the primary users,” she said. The group realized they had not confirmed who held sign-off power. The missing stakeholder wasn’t active in daily work but still carried significant influence.
These patterns show how small gaps in awareness can disrupt progress. When teams rely on assumptions or familiar names, influential voices can be overlooked at critical moments. A more intentional approach gives teams a clearer understanding of how stakeholders think, influence decisions, and shape meaningful engagement.
The Real Work Behind Effective Stakeholder Management
Stakeholder management is more than assembling names. It requires understanding how each stakeholder thinks about the project and how much authority they hold. This clarity guides communication, expectations, and planning throughout the project lifecycle.
Several characteristics help clarify how each stakeholder influences progress and contributes to the work.
Key stakeholder characteristics
- Influence level: ability to approve, redirect, or block work.
- Interest level: motivation to stay involved or contribute feedback.
- Support stance: supportive, neutral, or resistant toward the effort.
- Internal or external role: location within or outside the organization.
- Functional impact: how the outcome affects their responsibilities.
Midway through the meeting, the PMO manager pointed out a trend. “We assumed people would speak up if they had concerns,” she said. “They usually wait until we ask.” Her reflection underscored the value of proactive engagement, especially in organizations with busy leaders.
These traits help teams shift from reactive updates to intentional engagement. Clear expectations reduce surprises that slow progress and create confusion. With a stronger structure, teams can see how engagement choices influence momentum and outcomes. That clarity supports steady stakeholder work across the project.
How Stakeholders Shape Project Outcomes More Than You Realize
Strong stakeholder engagement shapes outcomes by aligning expectations early. It strengthens communication and supports readiness for change. When people feel informed and included, they’re more likely to support decisions that move the project forward.
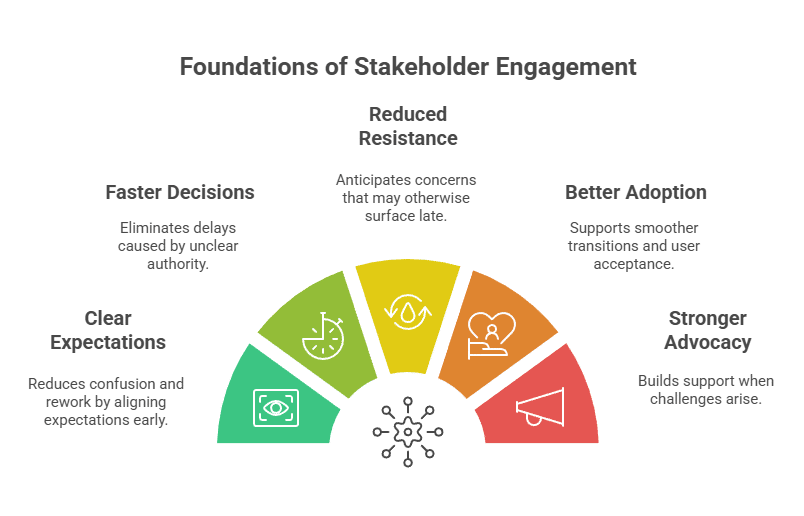
These benefits stand out even more when you look at how strong engagement supports delivery.
Key ways engagement strengthens delivery
- Clearer expectations: reduces confusion and rework.
- Faster decisions: eliminates delays caused by unclear authority.
- Reduced resistance: anticipates concerns that may otherwise surface late.
- Better adoption: supports smoother transitions and user acceptance.
- Stronger advocacy: builds support when challenges arise.
As the meeting continued, the CIO highlighted the impact on trust. “People assume we skipped steps,” she said. “Engagement affects trust as much as delivery.” Her comment shifted the team’s focus toward the process gaps that allowed the oversight.
When teams see how engagement supports stability, they recognize the need for structure. A clearer path reduces ambiguity and helps keep conversations focused on shared goals. This focus helps work stay steady when challenges arise. With that clarity, a defined stakeholder process becomes essential.
A Clear, Repeatable Stakeholder Management Process That Works
A structured process strengthens stakeholder engagement and reduces delays. It helps project managers understand who shapes decisions and how influence works. With a clear framework, teams can adjust more easily when priorities shift.
A clear process helps teams bring structure and predictability to stakeholder work, and these four steps offer a dependable path to follow.
1. Identify Stakeholders
Identifying stakeholders starts with knowing who benefits from the work and who influences its direction. This step takes more than familiar names. Teams must examine functional impact, decision rights, and each role’s connection to outcomes. A clear list gives teams a solid foundation for sound decisions.
Several sources can help teams build a complete view of potential stakeholders.
Useful stakeholder sources
- Org structure: reveals reporting lines and authority relationships.
- Process owners: highlight workflow changes affecting daily operations.
- External partners: identify dependencies that shape technical or contractual work.
- Regulatory roles: ensure compliance expectations are included early.
- Approval paths: clarify who guides or authorizes final decisions.
2. Analyze Interests and Influence
Analysis helps teams understand how each stakeholder views the project and how their authority affects progress. It clarifies who needs close involvement, who needs updates, and who shapes decisions. The goal is to align engagement with each person’s influence and interest.
A few targeted questions can clarify and make the analysis more consistent.
Key analysis questions
Decision impact: how the project changes their responsibilities or outcomes.
- Authority level: influence over direction, scope, or approvals.
- Engagement style: expected responsiveness or communication patterns.
- Core concerns: issues they may raise at critical moments.
- Matrix position: where they belong in the power/interest model.
3. Develop an Engagement Plan
An engagement plan defines how communication will flow throughout the project. It sets expectations for timing, format, and decision roles so teams follow a clear structure. These routines reduce confusion and help teams adjust with confidence when needs shift.
A strong plan includes several elements that keep communication focused and predictable.
Plan components to define
- Update cadence: the frequency with which each stakeholder receives information.
- Communication channels: aligns the message type with the right format.
- Decision roles: clarifies who approves, advises, or informs.
- Feedback loops: defines how input will be gathered and reviewed.
- Escalation routes: supports clear action when priorities conflict.
4. Execute and Adapt
Execution centers on keeping alignment as conditions change. Stakeholder engagement often shifts with workload, priorities, or new concerns. Teams need to watch for these signals and adjust communication to keep relationships steady and clear. This awareness helps prevent issues that can disrupt momentum.
Specific signals can show when stakeholder engagement is changing.
Common engagement signals
- Slower replies: responses take longer than usual without an apparent reason.
- Delegated attendance: substitutes attend meetings in place of key voices.
- Reduced feedback: comments become shorter or less detailed.
- Rising confusion: more questions emerge about scope or timing.
- Early hesitation: subtle signs of concern appear in discussions.
The PMO manager paused on the impact of the earlier oversight. “We relied on routine instead of structure,” she said. The team realized that more precise analysis and engagement would have revealed the missing stakeholder sooner. They committed to using this process to guide future work.
Even strong processes can slip without consistent attention. These pitfalls can slow progress and create instability at key moments. Understanding them early helps teams work with more awareness and discipline. That insight sets up the challenges that often disrupt stakeholder work.
The Stakeholder Mistakes That Quietly Derail Good Projects
Even with a clear process in place, teams can still misstep as work progresses. Minor missteps can escalate into delays or confusion when pressure rises. Recognizing these patterns helps teams spot risks earlier and adjust with more confidence. With that awareness, common stakeholder mistakes become easier to prevent.
Several missteps appear more often than teams expect.
Frequent mistakes to avoid
- Late identification: missing key roles during planning.
- Equal treatment: ignoring differences in influence and interest.
- Underestimating end users: overlooking daily workflow needs.
- Inconsistent communication: confusing teams with unclear patterns.
- Unresolved conflicts: postponing decisions that require alignment.
- Static stakeholder lists: ignoring role changes or team movement.
As the group compared past projects, the HR director raised an issue they had overlooked. “We underestimated how much people’s roles shift,” she said. “Promotions and reassignments change influence.” Her insight reminded the team that engagement is dynamic and requires regular updates.
Recognizing these missteps highlights the value of consistent tools and disciplined habits. Structured engagement makes communication clearer and supports stronger alignment. This stability gives teams a solid base and naturally leads to the tools that reinforce these habits.
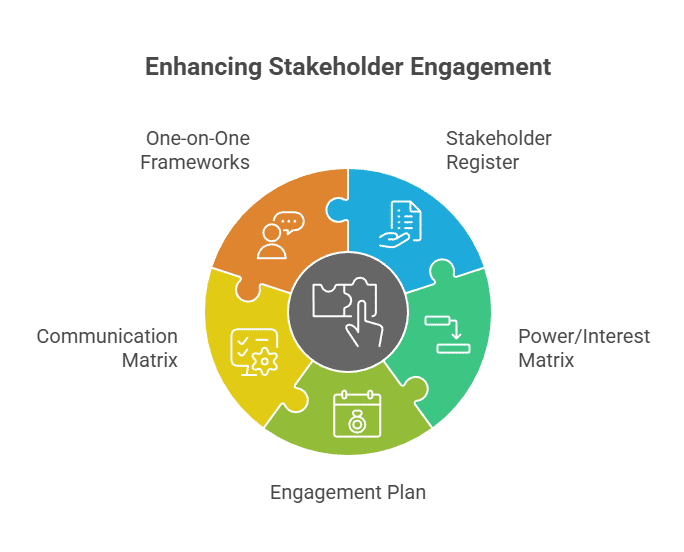
Essential Tools and Practices for Stronger Stakeholder Work
Stakeholder work becomes easier when teams use tools that bring clarity and structure to their communication. These resources help reduce uncertainty and maintain steady routines as conditions shift. With the right tools in place, engagement becomes more consistent throughout the project.
Several tools can help teams maintain structure and strengthen engagement.
Useful tools and templates
- Stakeholder register: captures names, roles, and influence.
- Power/Interest Matrix: supports analysis and prioritization.
- Engagement plan: defines cadence and authority.
- Communication matrix: clarifies expectations and detail levels.
- One-on-one frameworks: help manage high-risk conversations.
Toward the end of the discussion, the CTO reviewed engagement indicators from past work and noted a clear trend. “Our escalations dropped when stakeholders engaged early,” he said. His reflection highlighted how structured analysis and communication strengthened coordination and reduced last-minute surprises.
These tools help teams build habits that make engagement more reliable. When used consistently, they strengthen the clarity teams need to navigate complexity. This consistency supports steadier outcomes and more reliable delivery. SentinelWave’s experience shows how these habits lead to measurable improvement.
How Strong Stakeholder Work Builds More Predictable Projects
Strong stakeholder management brings stability throughout delivery. It gives teams a clear view of decision-makers, influence, and key communication needs. These habits reduce uncertainty and keep work aligned. When practiced consistently, they create steadier outcomes across projects.
Six months later, SentinelWave saw clear progress. Their stakeholder lists became more accurate, engagement routines strengthened, and delays across teams decreased. What began as a missed consultation became a reminder of the stability that disciplined processes create.
Strong stakeholder management helps teams move through uncertainty with confidence. It reduces risk, improves communication, and creates the clarity needed for successful delivery.
Are you ready to improve your stakeholder relationships?
If you want fewer delays and more predictable outcomes, start with stronger stakeholder management.
Project Management Academy provides instructor-led courses that equip you with the frameworks, communication techniques, and practical tools today’s projects demand. Take the next step toward leading more aligned, efficient, and successful projects.


 New Horizons
New Horizons
 Project Management Academy
Project Management Academy
 Six Sigma Online
Six Sigma Online
 TCM Security
TCM Security
 TRACOM
TRACOM
 Velopi
Velopi
 Watermark Learning
Watermark Learning
 Login
Login




 New Horizons
New Horizons
 Project Management Academy
Project Management Academy
 Velopi
Velopi
 Six Sigma Online
Six Sigma Online
 TCM Security
TCM Security
 TRACOM
TRACOM
 Watermark Learning
Watermark Learning