The PMBOK® Guide is undergoing its biggest transformation in years, and the project management world is paying close attention. Scheduled for release in early 2026, PMBOK 8 brings back clarity and practical structure while keeping the flexible, value-focused mindset introduced in PMBOK 7.
The Seventh Edition advanced the profession, but many practitioners felt it left too much room for interpretation and not enough guidance for everyday project work. PMBOK 8 addresses that feedback by sharpening the principles, refining the performance domains, and reintroducing nonprescriptive processes that support real project environments.
So what is changing, and why does it matter? Below is a clear breakdown of what PMBOK 8 includes, how it improves earlier editions, and what it means for project managers today.
What Is PMBOK 8th Edition?
The PMBOK® Guide Eighth Edition is PMI’s newest update to the global standard for project management. This edition is grounded in extensive research, including approximately 48,000 data points gathered in 2023 from practitioners, industry leaders, and organizations around the world. The result is a guide shaped by real project environments and the challenges professionals face every day.
PMI designed the Eighth Edition to be more accessible, more streamlined, and more adaptable. It works across industries and delivery methods, including predictive, agile, and hybrid project environments. The goal is to give project managers a clearer, evidence-backed standard they can apply immediately, with guidance that supports both strategic decision making and day-to-day project execution.
At a high level, the major updates fall into four categories. These include new terminology and concept refinements, a simplified set of core principles, the reintroduction of Process Groups in the form of Focus Areas, and an updated set of Project Management Performance Domains. Together, these changes make PMBOK 8 a more cohesive and practical resource for modern project work.
The Six Project Management Principles
The Eighth Edition introduces a streamlined set of six project management principles. These principles were reduced and refined from the twelve in the Seventh Edition to eliminate overlap and create a clearer decision-making foundation. Each principle is designed to guide behavior across every type of project environment, whether predictive, adaptive, or hybrid.
The six principles are:
| Principle | What It Emphasizes |
| Adopt a Holistic View | Encourages systems thinking and awareness of how project decisions affect the larger organizational environment. |
| Focus on Value | Reinforces that project success is measured by outcomes that matter to stakeholders, not just completing tasks. |
| Embed Quality | Promotes proactive integration of quality into both processes and deliverables throughout the project lifecycle. |
| Be an Accountable Leader | Combines stewardship and leadership behaviors to support responsible decisions and ethical project governance. |
| Integrate Sustainability | Emphasizes environmental, economic, and social considerations as part of responsible project management. |
| Build an Empowered Culture | Encourages collaboration, trust, psychological safety, and strong team performance. |
A Stronger Focus on Outcomes and Value
PMBOK 8 places significant emphasis on value delivery. Rather than centering success on outputs alone, the guide encourages project managers to think in terms of outcomes that are worth the investment of time, cost, and effort. This includes attention to quality, stakeholder satisfaction, sustainability, and alignment with organizational goals.
One of the most notable updates in the Eighth Edition is the reintroduction of a structure similar to Process Groups. In PMBOK 8, these are presented as Project Management Focus Areas, which describe the core activities that occur throughout any project. The Focus Areas are practical, familiar, and intentionally flexible, allowing them to apply in predictive, agile, and hybrid environments.
The five Focus Areas are:
- Initiating
Establishing the project vision, purpose, and alignment with organizational strategy. - Planning
Defining the approach, building estimates, identifying risks, establishing governance, and preparing for execution. - Executing
Performing the work needed to achieve project objectives while managing teams, stakeholders, and resources. - Monitoring and Controlling
Tracking performance, managing changes, correcting variances, and ensuring alignment with the plan. - Closing
Finalizing deliverables, completing administrative work, capturing lessons learned, and confirming value delivery.
These Focus Areas provide a logical flow for project work while leaving room to tailor activities to the project’s method, complexity, and context.
Seven Project Management Performance Domains
PMBOK 8 organizes key responsibilities into seven Project Management Performance Domains. These domains represent groups of related processes and practices that collectively support value delivery. They build on earlier concepts like Knowledge Areas but present them in a more integrated and practical way.
The seven performance domains are:
| Performance Domain | What It Emphasizes |
| Governance | Ensures appropriate oversight, decision making, compliance, and alignment with organizational policies. |
| Scope | Defines and manages the boundaries of the project, including quality expectations. |
| Schedule | Establishes timelines, sequences work, and supports the coordination of activities. |
| Finance | Manages budgeting, cost performance, financial stewardship, and investment decisions. |
| Stakeholders | Engages individuals and groups in ways that support shared understanding, collaboration, and value creation. |
| Resources | Covers the planning and management of people, materials, tools, and facilities required for project work. |
| Risk | Addresses uncertainty, threats, and opportunities through proactive planning and ongoing management. |
Within these domains, the Eighth Edition includes 40 non-prescriptive processes. These processes describe how work is commonly performed while still allowing project managers to tailor their approach based on the environment and needs of the project. The intent is to provide structure without rigidity.
Together, the principles, Focus Areas, and performance domains form the integrated structure of PMBOK 8. Each element supports the others, creating a practical framework that helps project managers think strategically and execute effectively.
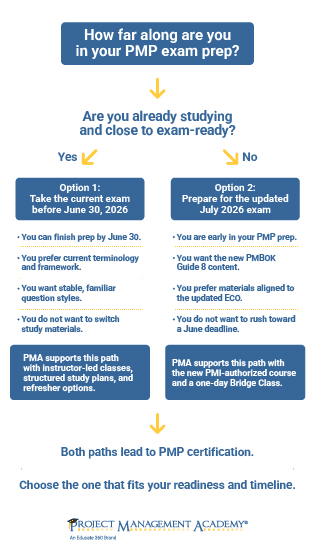
How PMBOK 8 Affects the PMP Exam Content Outline
With the release of the PMBOK® Guide Eighth Edition in early 2026, PMI is updating both the ECO and the exam experience to align with modern project expectations. These changes take effect on July 1, 2026, when the updated PMP exam officially launches.exa
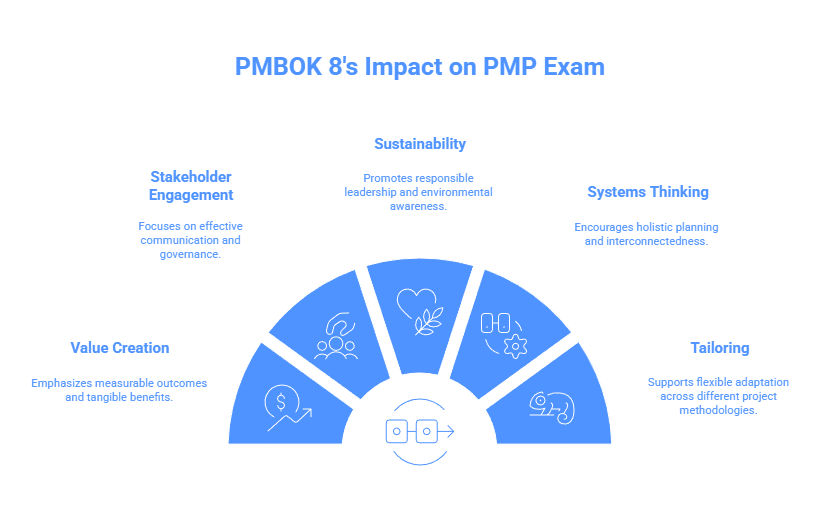
The revised ECO still uses the three-domain structure of People, Process, and Business Environment, but the focus within those domains shifts significantly. The new exam places greater emphasis on:
- Value creation and measurable outcomes
- Stakeholder engagement and governance
- Sustainability and responsible leadership
- Systems thinking and holistic planning
- Tailoring across predictive, agile, and hybrid delivery
PMI is also introducing a more interactive exam format with scenario sets, visual interpretation, and decision-focused question types. These updates mirror the themes of PMBOK 8, which blends principles, domains, and actionable processes to support better real-world decision making.
For candidates preparing for certification, understanding PMBOK 8 provides important context for how PMI expects project managers to think and lead. It aligns closely with the mindset behind the 2026 exam update and the skills the new ECO is designed to measure.
For a complete walkthrough of the July 2026 PMP exam changes, including timelines, new question types, and study recommendations, see our full guide: 2026 PMP Exam Update: What’s Changing and How to Prepare.
How PMBOK 8 Compares to Previous Editions
The PMBOK® Guide has evolved significantly over time, and the Eighth Edition represents a deliberate blending of what practitioners valued most from past versions. Earlier editions, such as the Sixth, offered detailed process guidance with Inputs, Tools and Techniques, and Outputs. The Seventh Edition shifted toward a more flexible, principle-driven approach that emphasized value delivery but left many teams wanting more practical structure.
PMBOK 8 integrates these two perspectives. It preserves the adaptability introduced in the Seventh Edition while reintroducing process clarity in the form of nonprescriptive practices. This combined approach provides a complete framework that supports both strategic thinking and day-to-day execution, and it works across predictive, agile, and hybrid environments.
The result is a more intuitive, structured standard that keeps the flexibility of PMBOK 7 while adding the practical direction teams have been asking for. For a deeper side-by-side comparison, see our full PMBOK 7 vs PMBOK 8 blog.
The Key Takeaway for Practitioners
The PMBOK® Guide Eighth Edition brings together clarity, flexibility, and practical guidance in a way that supports every type of project environment. Its structure gives project managers a complete view of the work they lead. The principles and Focus Areas reinforce the strategic and behavioral mindset needed for modern delivery, while the performance domains and nonprescriptive processes provide the mechanics for effective execution.
Get Ready for the 2026 PMP® Exam Changes With a Clear Plan
The PMBOK® Guide Eighth Edition brings big updates to the PMP exam, and the right timeline depends on where you are in your career and how you prefer to learn. As a Premier ATP closely aligned with PMI, Project Management Academy receives updated materials before most providers, and we help you navigate exactly what these changes mean.
Whether you’re preparing now or planning for the new 2026 exam version, PMA will guide you in choosing the right study path and exam window for your success.
FAQS
When will PMBOK 8 be released?
PMI has announced that the PMBOK® Guide Eighth Edition will be released in early 2026, with related PMP exam updates taking effect on July 1, 2026. Many project managers are watching closely because this release represents the biggest structural update since the shift to principles in PMBOK 7.
How is PMBOK 8 different from PMBOK 7?
PMBOK 8 brings back more structure and practical guidance. It introduces 6 streamlined principles, 7 updated performance domains, 5 Focus Areas (similar to Process Groups), and 40 nonprescriptive processes. The goal is to combine the flexibility of PMBOK 7 with the clarity and “how-to” guidance practitioners missed from older editions.
Will the PMP exam change because of PMBOK 8?
Yes. PMI is updating the PMP exam to align with PMBOK 8, launching the new exam version on July 1, 2026. The updated ECO increases emphasis on value delivery, governance, sustainability, stakeholder engagement, and tailoring across predictive, agile, and hybrid environments.
Do I need to study PMBOK 8 to pass the PMP exam now?
Not yet. Candidates taking the PMP exam before July 1, 2026 will continue using the current exam version. PMBOK 8 only impacts the exam after that date. Those preparing now can safely use current study materials and take the exam before the transition window.
What practical impact will PMBOK 8 have on my day-to-day project work?
PMBOK 8 emphasizes value delivery, systems thinking, governance, and sustainability—meaning it encourages more strategic decision-making. Its Focus Areas and nonprescriptive processes offer clearer guidance on how to plan, execute, monitor, and close projects while still allowing full tailoring for agile, predictive, and hybrid environments.


 New Horizons
New Horizons
 Project Management Academy
Project Management Academy
 Six Sigma Online
Six Sigma Online
 TCM Security
TCM Security
 TRACOM
TRACOM
 Velopi
Velopi
 Watermark Learning
Watermark Learning
 Login
Login




 New Horizons
New Horizons
 Project Management Academy
Project Management Academy
 Velopi
Velopi
 Six Sigma Online
Six Sigma Online
 TCM Security
TCM Security
 TRACOM
TRACOM
 Watermark Learning
Watermark Learning